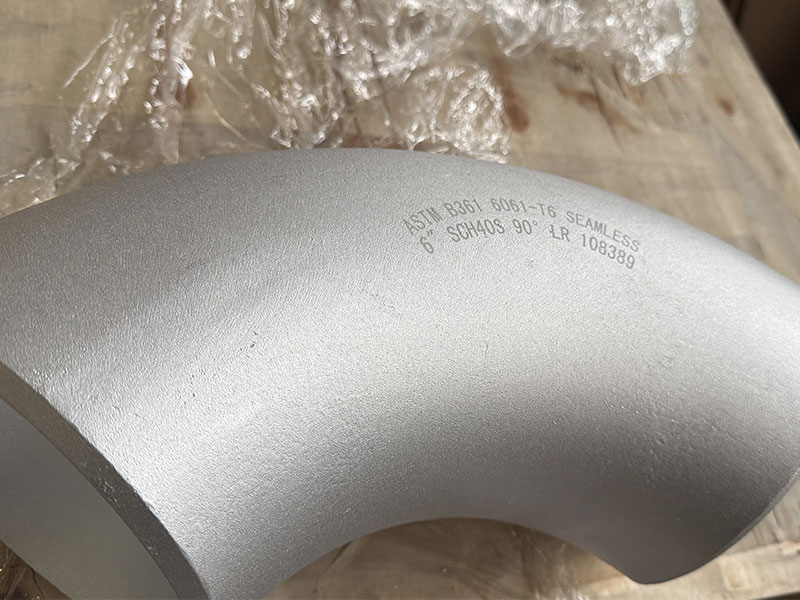
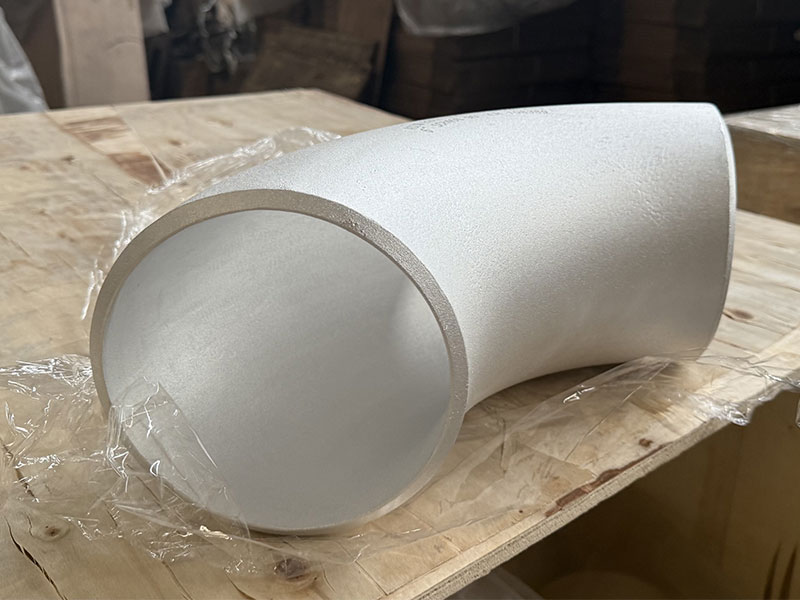
Marine Aluminum Elbow for Exhaust Ventilation Systems
Marine aluminum elbows are precision-formed duct components designed specifically for exhaust and ventilation systems aboard commercial ships, yachts, offshore platforms, and other marine environments. Manufactured from marine-grade aluminum alloys and produced with corrosion-resistant fabrication techniques, these elbows combine lightweight construction, excellent corrosion resistance, and high thermal performance to meet the demanding conditions of sea-going applications.
Marine Aluminum Elbows provide lightweight, corrosion-resistant duct transitions for shipboard exhaust and ventilation systems. Made from marine-grade aluminum alloys (commonly 5083, 5052, 6061), they offer excellent strength-to-weight ratio, saltwater corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and easy fabrication. Available in tight radii, mitre, and long-radius forms with multiple end configurations and custom flanges, they are ideal for engine rooms, galley exhaust, HVAC and bilge ventilation. Typical specs include wall thicknesses from 1.5–6.0 mm, operating temperature up to 200 °C (short-term higher), and design pressures up to mild positive/negative ventilation requirements.
Features
- Corrosion-resistant marine-grade aluminum alloys optimized for saltwater environments.
- Lightweight—reduces ship mass and eases handling during installation and maintenance.
- High thermal conductivity for controlled heat dissipation in exhaust systems.
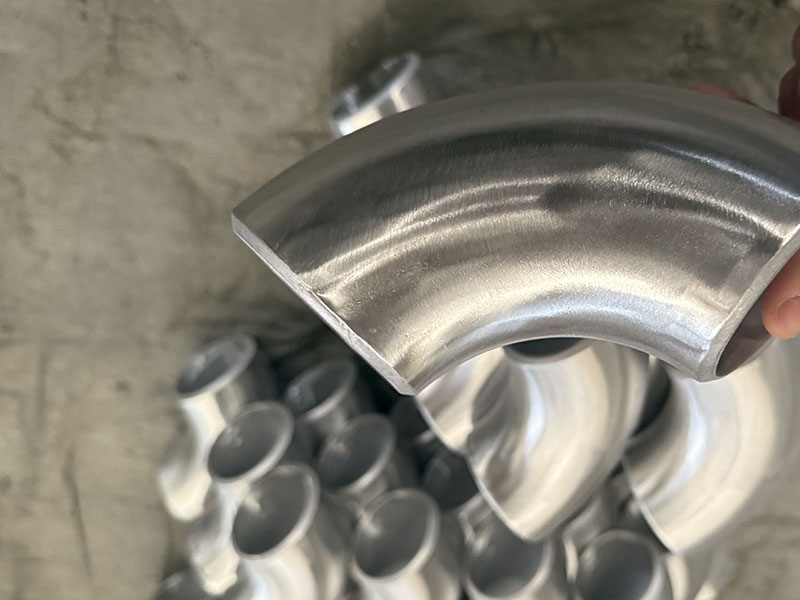
- Multiple elbow types: 45°, 90°, 30°, long-radius, short-radius, mitre, segmented, and swaged.
- End connections: slip-fit, flange, bead-and-groove, beaded ends for coupling, or custom weld collars.
- Available in seamless-bent or welded segmented construction depending on diameter and thickness.
- Heat-treated or cold-worked alloy options for different strength/ductility balances.
- Surface finishes: mill, anodized, epoxy- or polyurethane-coated, or alodine conversion coating for improved corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
- Compliance options for marine standards (e.g., ABS, Lloyd’s Register, DNV, ISO 9001 manufacturing control).
- Custom fabrication for routing around structural members and system constraints.
- Recyclable and environmentally friendly material.
Typical Applications
- Engine room exhaust and ventilation ducting.
- Galley exhaust systems and range hood ductwork.
- HVAC supply and return transitions in cabins and machinery spaces.
- Bilge ventilation and odor control ducts.
- Tailpipe/exhaust outlets for auxiliary generators.
- Fire-smoke control ductwork (subject to fire-rating and regulatory approvals).
- Outlets/pass-throughs to superstructure where lightweight and corrosion resistance are required.
Materials & Alloy Options
Common marine aluminum alloys used for elbows:
| Alloy | Typical Use | Corrosion Resistance | Strength Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5083 (H111/H116) | Structural and marine ducting | Excellent in seawater | High strength and good fatigue resistance |
| 5052 (H32/H34) | Formable ducting, smaller diameters | Very good, especially anodized | Good formability and moderate strength |
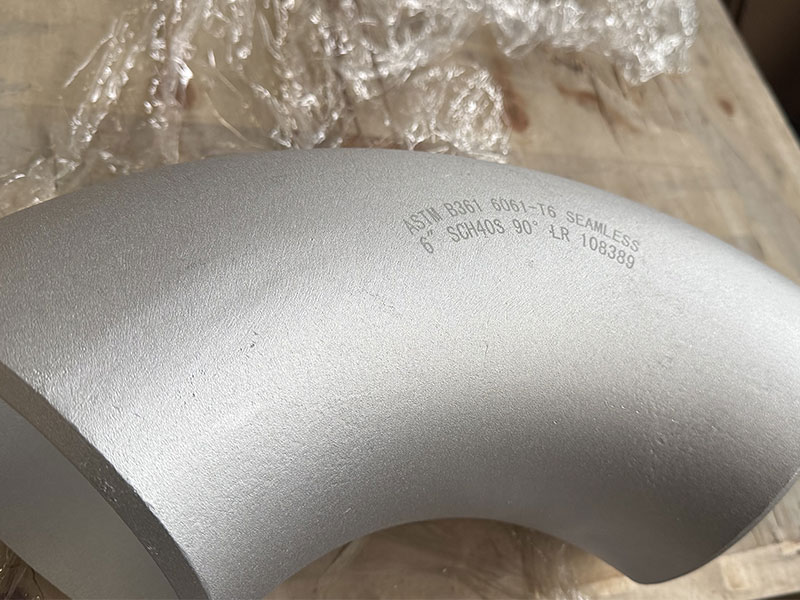
| 6061-T6 / T651 | Higher strength needs, flanges, fittings | Good when coated; less than 5xxx alloys | Higher yield & tensile strength; heat-treatable |
| 3003 / 3004 | Light-duty, low-cost ducts | Moderate | Highly formable; lower strength |
Notes:
- 5xxx series (e.g., 5083, 5052) are preferred for seawater corrosion resistance.
- 6061 is used where higher strength and better machinability for flanges are required; often coated for corrosion protection.
Chemical Composition (Representative ranges)
Note: Table shows typical composition ranges for alloys commonly used in marine elbows. Values are approximate; consult specific material certificates for exact composition.
| Element (%) | 5083 (approx.) | 5052 (approx.) | 6061 (approx.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Al (balance) | 94.8–97.9 | 97.0–98.5 | 97.9–99.0 |
| Mg | 4.0–4.9 | 2.2–2.8 | 0.8–1.2 |
| Mn | 0.4–1.0 | 0.1–0.5 | 0.15–0.4 |
| Si | 0.4 max | 0.25 max | 0.4–0.8 |
| Fe | 0.4 max | 0.4 max | 0.7 max |
| Cu | 0.1 max | 0.1 max | 0.15–0.4 |
| Cr | 0.05–0.25 | 0.15–0.35 | 0.04–0.35 |
| Zn | 0.25 max | 0.25 max | 0.25 max |
| Ti | 0.05 max | 0.03 max | 0.15 max |
Mechanical & Thermal Properties
Representative mechanical and thermal properties for common alloys (typical values):
| Property | 5083-O/H116 | 5052-H32 | 6061-T6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density (g/cm3) | 2.66 | 2.68 | 2.70 |
| Yield Strength (MPa) | 215–275 (temp-dependent) | 125–215 | 240–275 |
| Tensile Strength (MPa) | 290–350 | 210–265 | 310–350 |
| Elongation (%) | 12–18 | 5–20 | 8–12 |
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | ~121 | ~138 | ~167 |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion (10^-6 /K) | 23.3 | 23.1 | 23.6 |
| Operating Temperature (continuous) | -200 to 150 °C* | -200 to 150 °C* | -50 to 120 °C* |
*Short-term exposures (exhaust pulses) can be higher; consult alloy provider for creep and temper limits.
Typical Sizes, Thicknesses & Radii
| Parameter | Typical Range |
|---|---|
| Nominal Diameter (ID) | 50 mm to 1000+ mm (2" to 40"+) |
| Wall Thickness | 1.5 mm to 6.0 mm (0.060" to 0.250") typical; thicker for structural/pressure needs |
| Bend Radii | Short-radius: 1D; Long-radius: 1.5D–3D; Custom radii available |
| Bend Angle Options | 15°, 30°, 45°, 60°, 75°, 90°, 180° (return) |
| Seam Type | Longitudinal welded, circumferential seams for segmented elbows, or seamless bent smaller sizes |
| Flange Types | ASME/ISO flanges, welded collar flanges, loose flanges, or custom bolted flange adapters |
Fabrication & Finishing Options
- Fabrication: spinning, roll-forming, press-bending for small diameters; segmented welding (mitre) with TIG/MIG for larger sizes; hydroforming or stretch-bending for special shapes.
- Welding: TIG (GTAW) recommended for high-quality welds in aluminum; filler alloys matched to base metal (e.g., ER5356 for 5xxx series).
- Heat treatment: limited for 5xxx series (work-hardened tempers common); 6061 often solution-treated then aged (T6/T651).
- Surface treatments:
- Alodine/Chemical conversion coating for corrosion resistance and paint adhesion.
- Anodizing (where applicable) for enhanced surface hardness and corrosion resistance (note: effectiveness in seawater varies by alloy).
- Powder coat or marine-grade epoxy/polyurethane paint systems for additional protection and aesthetics.
- Insulation: thermal or acoustic insulation liners (rockwool or mineral wool with foil facing) available for hot exhaust ducts.
- Accessories: access panels, inspection ports, drain points (condensate drip pans), vibration isolators, and flexible metal connectors.
Installation & Maintenance Notes
- Ensure proper alignment and support spacing based on duct weight and dynamic loads; use resilient mounts for vibration isolation near engine/generator exhausts.
- Thermal expansion: include slip joints or expansion loops where long runs or temperature swings occur.
- Corrosion prevention: prefer 5xxx series alloys or apply suitable coatings in highly corrosive zones; avoid galvanic couples with dissimilar metals without isolation.
- Drainage: provide low points and drain ports to remove condensate and prevent pooling.
- Fire safety: aluminum has lower melting point than steel—verify fire-rating requirements and ensure compliance with SOLAS, Class rules, and local regulations for fire barriers and dampers.
- Inspection: check welds, coatings, and fasteners regularly; repair surface damage promptly to prevent localized corrosion.
- Cleaning: use non-abrasive cleaners; avoid concentrated alkaline solutions that can attack aluminum under some conditions.
Performance Limits & Design Considerations
- Pressure: generally suitable for low-pressure ventilation and exhaust. For positive-pressure HVAC ducts or code-driven pressure ratings, design and thickness must be verified.
- High-temperature exposure: continuous temperatures in typical HVAC/exhaust are acceptable up to ~120–150 °C for 5xxx alloys; pulsed exhaust temperatures from engine systems may be higher — use heat-resistant insulation and check alloy temper limits.
- Galvanic corrosion: isolated from steel and copper with gaskets, coatings, or insulating washers when contacting dissimilar metals.
- Structural load: larger diameter elbows with thin walls may require reinforcement rings or stiffeners when spanning unsupported sections.
Typical Technical Specification (Sample)
| Spec Item | Typical Requirement |
|---|---|
| Material | 5083-H116 or 5052-H32 (as specified) |
| Wall Thickness | 2.0 mm (standard) — other thickness per design |
| Elbow Type | 90° long-radius (1.5D) mitre-welded segmented |
| Ends | Beaded ends for clamp coupling; optional ANSI/ISO flange |
| Welding | TIG (GTAW) with ER5356 filler for 5xxx series |
| Surface Finish | Alodine conversion + primer + polyurethane topcoat (RAL specified) |
| Max Continuous Temperature | 150 °C (design dependent) |
| Certification | Manufactured under ISO 9001; options for ABS/DNV certification |
Example Product Variants
- 90° Long-Radius Marine Elbow, 200 mm ID, 2.5 mm 5083-H116, beaded ends, alodine + paint.
- 45° Short-Radius Exhaust Elbow, 150 mm ID, 6061-T6 with welded flange, insulated jacket.
- Segmented 90° Large-Diameter (800 mm) exhaust elbow, 3 mm 5052-H32, TIG welded, primer-coated inside/outside.
- Mitred Multi-Segment Elbow with integrated drain and inspection port for galley exhaust.
Ordering Considerations
When ordering, provide:
- Nominal internal diameter and required wall thickness.
- Bend angle and radius (short/long or radius factor e.g., 1.5D).
- Alloy and temper specification.
- End connection type and flange standards (if any).
- Surface treatment/coating requirements and color (if painted).
- Maximum operating temperature and environment (exhaust, salt spray).
- Any special accessories: insulation, drains, inspection ports, vibration isolators.
- Certification needs (class society approval, material test reports).
Safety & Regulatory Considerations
- Confirm compliance with marine class society rules (ABS, DNV, Lloyd’s) for structural or exhaust components if required by vessel or installation.
- For engine exhaust systems, ensure components meet gas-tightness, heat shielding, and fire-damage tolerance as specified by project engineering and regulations.
- Verify compatibility with onboard fire detection/suppression systems and ensure access for inspection and emergency service.
If you want, I can provide:
- A downloadable sample specification sheet (PDF-ready) tailored to your vessel class.
- A table of recommended fasteners, gaskets and clamps for specific alloy pairings.
- CAD-ready dimensional templates for common elbow sizes (DWG/STEP).
Which of these would be most useful?
Related Products
Custom marine aluminum profile tubes
Custom Marine Grade Aluminum Profile Tubes are manufactured from premium marine aluminum alloys such as 5083, 5052, 6061, and 6082.
View Details6061-T6 90-Degree Marine Aluminum Pipe Elbow
Manufactured from premium 6061-T6 marine-grade aluminum alloy, this elbow fitting is engineered to provide reliable and efficient pipe direction changes within shipbuilding, offshore platforms, and marine infrastructure systems.
View DetailsMarine aluminum round tubes
Marine Grade Aluminum Round Tubes are manufactured from premium marine alloys such as 5083, 5052, 6061, and 6082, all selected for their proven resistance to seawater corrosion and marine atmosphere degradation.
View DetailsMarine aluminum square tubes
Marine Grade Aluminum Square Tubes are typically constructed from marine-grade alloys such as 5083, 5052, 6061, and 6082—well-known for their ability to withstand the aggressive effects of saltwater and marine atmospheres.
View DetailsMarine aluminum rectangular tubes
Marine Grade Aluminum Rectangular Tubes are made from high-performance alloys such as 5083, 5052, 6061, and 6082. These alloys are renowned for their ability to resist corrosive seawater and marine atmospheres while providing excellent mechanical strength and toughness.
View DetailsRelated Blog
Marine Aluminum Pipe Elbow for High Flow Desalination Units
In the rapidly advancing realm of seawater desalination, marine aluminum pipe elbows play a pivotal role in ensuring the smooth and efficient operation of high flow desalination units.
View DetailsMarine Aluminum Elbow for Combustion Air Supply Systems
In the demanding environment of marine vessels, reliable components contribute immensely to safety, efficiency, and longevity. Among such vital parts.
View DetailsCustom Marine Aluminum Elbow Fittings for Marine Industry
Custom marine aluminum elbow fittings are specialized pipe and tube fittings engineered for use in harsh marine environments. Designed to change the direction of fluid, air, or cable runs on vessels, offshore platforms, and coastal installations.
View DetailsMarine Aluminum Pipe Elbow for Desalination Plant Connections
In modern desalination plants, the choice of piping components is critical to ensuring efficiency, longevity, and resistance to harsh marine environments.
View DetailsAluminum Pipe Elbow for Shipboard Refrigeration Lines
In the world of marine refrigeration systems, maintaining integrity, durability, and corrosion resistance is critical to ensure onboard equipment functions on long sea voyages.
View DetailsMarine Aluminum Elbow for Fuel System Installations
When it comes to designing and installing fuel systems in marine environments, using the right materials is paramount. Among these materials, Marine Aluminum Elbows is know due to their remarkable properties and advantages.
View Details









Leave a Message